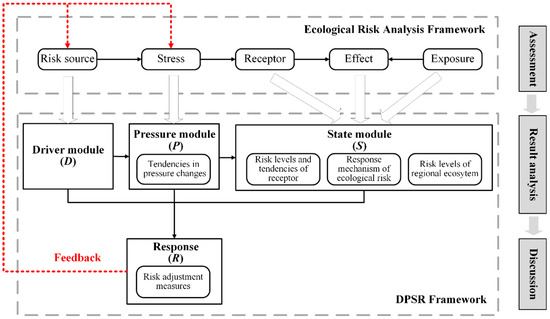
Atmospheric nitrogen deposition can supply nitrogen for ecosystems while posing a serious threat to ecological security. An assessment of the ecological risks caused by atmospheric nitrogen deposition is critical for urban sustainable development. Based on “Ecological Risk Analysis” and the “Driver-Pressure-State-Response (DPSR) framework,” this paper established a comprehensive ecological risk assessment model and assessed the ecological risk of nitrogen deposition in Xiamen City, China. The results showed that the risk from nitrogen deposition to the forest ecosystem is high due to the impact of nitrogen deposition on the residual rate of litter and survival rate of seedlings. The risks to freshwater and marine ecosystems were determined to be high and moderate, respectively, due to the promotion of eutrophication by nitrogen. The risk to farm ecosystems was low due to the impact on weeds. The proportion of high-risk areas in Xiamen City was 37.1%. Among the districts of Xiamen City, Tong’an and Xiang’an had the highest proportion of high-risk areas (48%) and low-risk areas (31.8%), respectively.