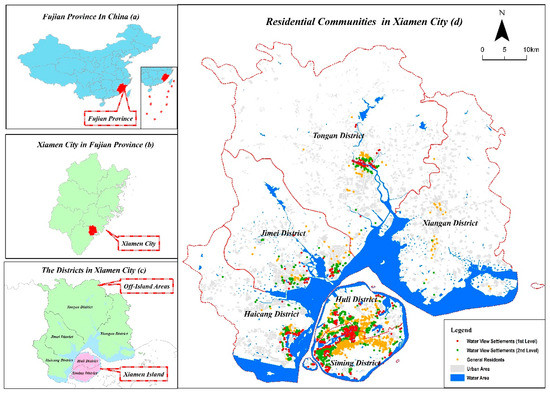
Suitable allocation of residential public services is vital to realizing sustainable communities and cities. By combining network big data and spatial analysis, we developed a composite spatial accessibility assessment method for residential suitability of urban public services covering healthcare, leisure, commerce, transportation, and education services. Xiamen City, China is the test site. We found that although most facilities were concentrated on Xiamen Island, there were shortages in the per capita transportation and education service supplements compared with the average performance of Xiamen City because of the high local population. Meanwhile, Tong’an had advantages in the amount of public facilities due to its long history of regional development. However, high-quality facilities were deficient there as well as in other off-island districts. The residential communities surrounding transportation, commerce, and healthcare facilities had a similar allocation pattern in Xiamen City, whereas the residential accessibility of education and leisure services showed regional differences. Due to unbalanced regional development, evident inequality could be witnessed by comparing the composite assessment results of residential suitability between the communities on Xiamen Island and those in the off-island Areas. Our study hopes to provide dedicated support for designing sustainable communities and cities, especially for those in developing countries.