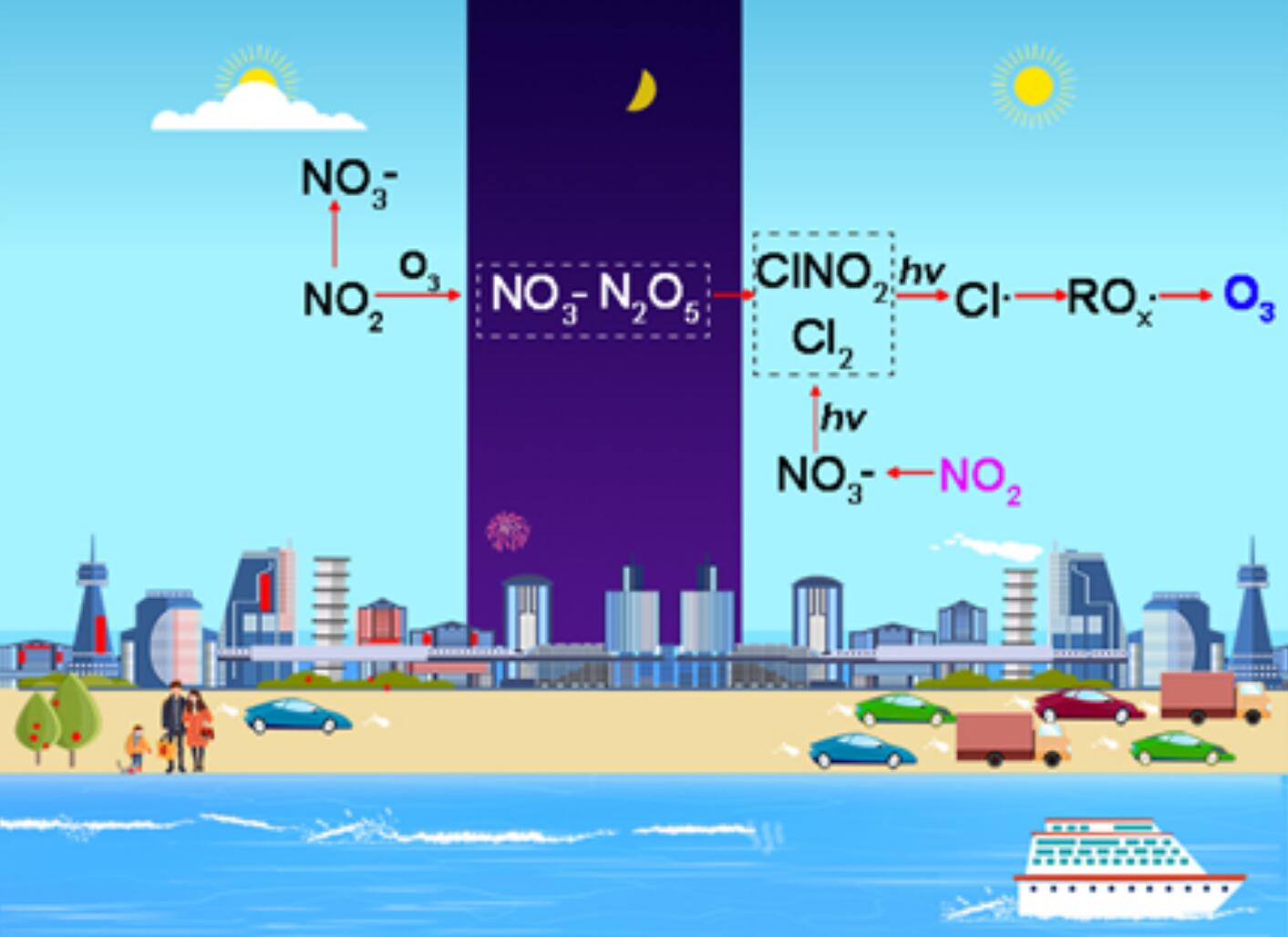
Chlorine (Cl) radicals strongly affect atmospheric oxidation and the fate of pollutants. Despite several observations, the potential impacts of nitrogen chemistry associated with NO2 on Cl chemistry are poorly understood. Here, we provided direct field evidence that the nitrogen chemistry enhancements triggered by the increased NO2 drove daytime nitrate (NO3-) photolysis and nighttime NO3-N2O5 reactions, significantly promoting the increases in the concentrations of ClNO2 and Cl2 after the Chinese Spring Festival. The enhancement in the Cl chemistry facilitated the elevations of both O3 and atmospheric oxidation capacity during the winter daytime. Our findings highlighted the importance of nitrogen chemistry induced by the increased NO2 in enhanced Cl chemistry.